ECONOMICS 101 - MICROECONOMICS
2 posters
Page 1 of 1
 Re: ECONOMICS 101 - MICROECONOMICS
Re: ECONOMICS 101 - MICROECONOMICS
Economics
- is the social science that deals with the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services and with the theory and management of economic systems.

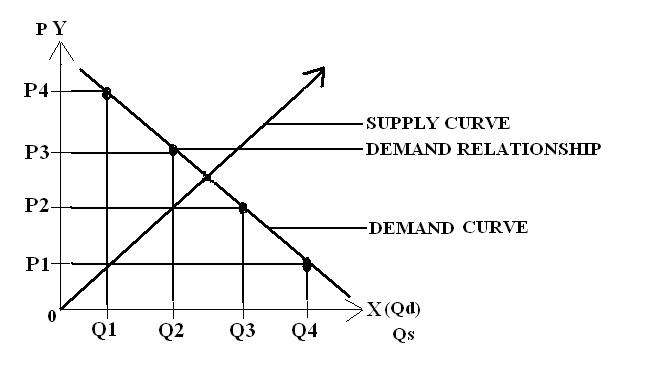
Demand – refers to how much of the product (quantity) or service is desired by buyers. The Quantity Demanded (Qd) is the amount of the product people are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity demanded is known as the demand relationship.
ECONOMIC RESOURCES
1. Land – refers to the ground that is used to build a structure such as factory, school, house or church but it means much more than that. Land is also the term used fro the rsources that come from the land.
a. Trees
Beverages, abaca
b. Vines
Chayote
c. Bush
corn, eggplant
d. Shrub
Tomatoes
e. Rocks
marbles, glass
f. Grass
Cogon, food for animals, Bermuda grass, ornamental grasses
g. water
springs and wells
h. caves
mines
i. seas and oceans
fishes, corals
j. air
oxygen, orchids, ornamentals
Land is also used for lumber, firewood, paper and other products. Minerals that came from the ground such as oil that is used for gasoline or to lubricate automobile engines or gold that is used to make jewelries or wheat that is grown on the ground and is used in the production of bread and other products.
2. Labor (Human Resources) – is the general category of the human effort that is used for the production of goods and services. This includes physical labor.
e.g. carpentry, fishing, mining, weaving, cattle raising, construction, dump services, manufacturing, selling, poultry raising, farming, planting, gardening, painting, writing, baking, cooking, photography, interviewing, dress-making, mechanics, electrician, automotive, engineering, astronomy, news casting, teaching, care giving, driving, designing
Mental Labor
e.g. interior designing, script writing, psychologists, teaching, psychiatrist, painting, management
3. Capital – is the input that is often viewed in 2 ways such as labor. Capital may be viewed as human capital or physical capital.
PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
PED – is the percentage change in Quantity Demanded if we change the Price.
- basic formula in Price Elasticity of Demand
- defined as the measure of responsiveness in the quantity demanded for a commodity as a result of change in Price.
- is the social science that deals with the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services and with the theory and management of economic systems.

Demand – refers to how much of the product (quantity) or service is desired by buyers. The Quantity Demanded (Qd) is the amount of the product people are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity demanded is known as the demand relationship.

ECONOMIC RESOURCES
1. Land – refers to the ground that is used to build a structure such as factory, school, house or church but it means much more than that. Land is also the term used fro the rsources that come from the land.
a. Trees
Beverages, abaca
b. Vines
Chayote
c. Bush
corn, eggplant
d. Shrub
Tomatoes
e. Rocks
marbles, glass
f. Grass
Cogon, food for animals, Bermuda grass, ornamental grasses
g. water
springs and wells
h. caves
mines
i. seas and oceans
fishes, corals
j. air
oxygen, orchids, ornamentals
Land is also used for lumber, firewood, paper and other products. Minerals that came from the ground such as oil that is used for gasoline or to lubricate automobile engines or gold that is used to make jewelries or wheat that is grown on the ground and is used in the production of bread and other products.
2. Labor (Human Resources) – is the general category of the human effort that is used for the production of goods and services. This includes physical labor.
e.g. carpentry, fishing, mining, weaving, cattle raising, construction, dump services, manufacturing, selling, poultry raising, farming, planting, gardening, painting, writing, baking, cooking, photography, interviewing, dress-making, mechanics, electrician, automotive, engineering, astronomy, news casting, teaching, care giving, driving, designing
Mental Labor
e.g. interior designing, script writing, psychologists, teaching, psychiatrist, painting, management
3. Capital – is the input that is often viewed in 2 ways such as labor. Capital may be viewed as human capital or physical capital.
PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
PED – is the percentage change in Quantity Demanded if we change the Price.
- basic formula in Price Elasticity of Demand
- defined as the measure of responsiveness in the quantity demanded for a commodity as a result of change in Price.
Last edited by RayMart on Sat May 02, 2009 11:28 pm; edited 2 times in total

RayMart- Posts : 111
Join date : 2009-04-25
Age : 34
Location : Baguio City, Philippines 2600
 Re: ECONOMICS 101 - MICROECONOMICS
Re: ECONOMICS 101 - MICROECONOMICS
1. Perfectly inelastic – not price sensitive
Goods demanded or quantity demanded is considered inelastic when the demand does not change no matter the price is set.
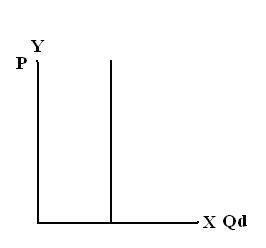
No matter how high or small the Price change is, there is no effect in Quantity Demanded
2. Relatively Inelastic – is an elastic alternative in which relatively large changes in Price cause relatively cause small changes in Quantity Demanded.
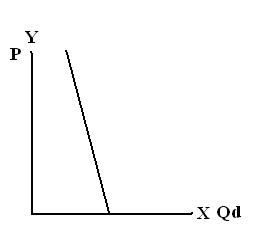
3. Unitary or Unit Elastic – an elasticity alternative in which percentage change in Price causes an equal percentage change in Quantity Demanded. Any change in Price whether big or small triggers exactly the same percentage change in Quantity Demanded.
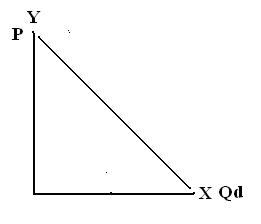
4. Relatively Elastic – an elasticity alternative in which relatively small change in Price causes relatively large change in Quantity Demanded. Quantity Demanded is very responsive to Price.
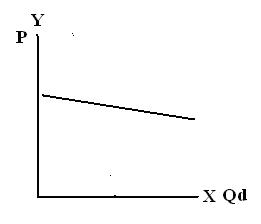
5. Perfectly elastic
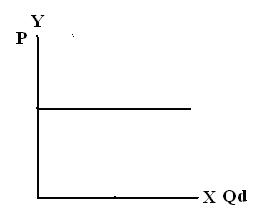
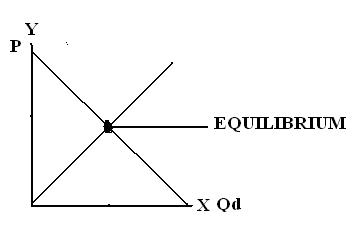
6. Equilibrium
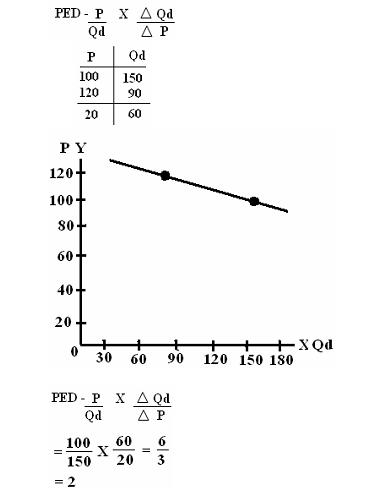
In every 1% increase in P, there is a 2 unit fall in constant demand.
For every 1% increase in the P, there is a corresponding 2 units fall in the change of products.
Goods demanded or quantity demanded is considered inelastic when the demand does not change no matter the price is set.

No matter how high or small the Price change is, there is no effect in Quantity Demanded
2. Relatively Inelastic – is an elastic alternative in which relatively large changes in Price cause relatively cause small changes in Quantity Demanded.
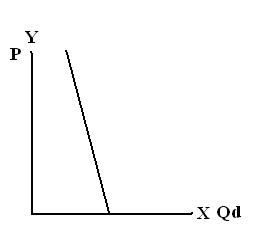
3. Unitary or Unit Elastic – an elasticity alternative in which percentage change in Price causes an equal percentage change in Quantity Demanded. Any change in Price whether big or small triggers exactly the same percentage change in Quantity Demanded.
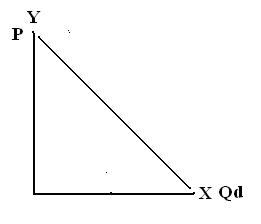
4. Relatively Elastic – an elasticity alternative in which relatively small change in Price causes relatively large change in Quantity Demanded. Quantity Demanded is very responsive to Price.
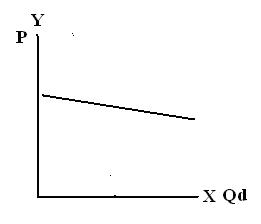
5. Perfectly elastic
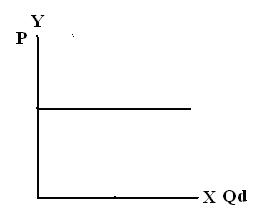
6. Equilibrium


In every 1% increase in P, there is a 2 unit fall in constant demand.
For every 1% increase in the P, there is a corresponding 2 units fall in the change of products.

RayMart- Posts : 111
Join date : 2009-04-25
Age : 34
Location : Baguio City, Philippines 2600
Page 1 of 1
Permissions in this forum:
You cannot reply to topics in this forum|
|
|

 Home
Home